Ovarian Cyst
What are ovarian cysts?
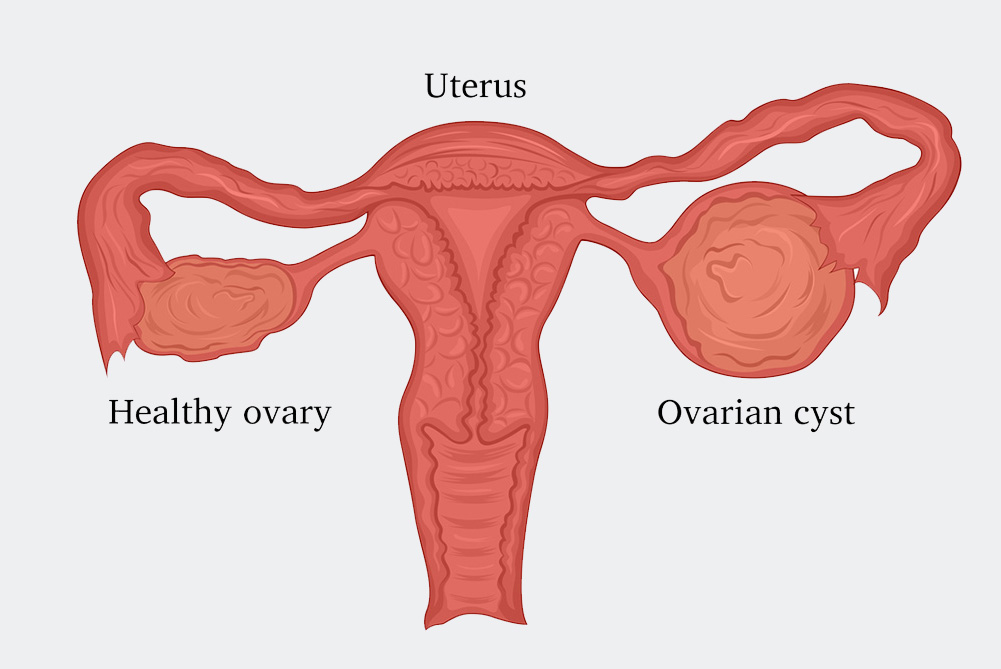
Most women will experience a cyst on the ovaries at least once, and most are painless, cause no symptoms, and are discovered during a routine pelvic exam. Symptoms of an ovarian cyst include nausea, vomiting, bloating, painful bowel movements, and pain during sex. In rare cases, an ovarian cyst can cause serious problems, so it’s best to have it checked by your doctor. The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. They’re located in the lower abdomen on both sides of the uterus. Women have two ovaries that produce eggs as well as the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Sometimes, a fluid-filled sac called a cyst will develop on one of the ovaries. Many women will develop at least one cyst during their lifetime. In most cases, cysts are painless and cause no symptoms.
Types of ovarian cysts.
There are various types of ovarian cysts, such as dermoid cysts and endometrioma cysts. However, functional cysts are the most common type. The two types of functional cysts include follicle and corpus luteum cysts.
Follicle cyst
During a woman’s menstrual cycle, an egg grows in a sac called a follicle. This sac is located inside the ovaries. In most cases, this follicle or sac breaks open and releases an egg. But if the follicle doesn’t break open, the fluid inside the follicle can form a cyst on the ovary.
Corpus luteum cysts
Follicle sacs typically dissolve after releasing an egg. But if the sac doesn’t dissolve and the opening of the follicle seals, additional fluid can develop inside the sac, and this accumulation of fluid causes a corpus luteum cyst.
Other types of ovarian cysts include:
- dermoid cysts: sac-like growths on the ovaries that can contain hair, fat, and other tissue
- cystadenomas: noncancerous growths that can develop on the outer surface of the ovaries
- endometriomas: tissues that normally grow inside the uterus can develop outside the uterus and attach to the ovaries, resulting in a cyst
Some women develop a condition called polycystic ovary syndrome. This condition means the ovaries contain a large number of small cysts. It can cause the ovaries to enlarge. If left untreated, polycystic ovaries can cause infertility.
Symptoms of an ovarian cyst
Often times, ovarian cysts do not cause any symptoms. However, symptoms can appear as the cyst grows. Symptoms may include:- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Painful bowel movements
- Pelvic pain before or during the menstrual cycle
- Painful intercourse
- Pain in the lower back or thighs
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe symptoms of an ovarian cyst that require immediate medical attention include:
- Severe or sharp pelvic pain
- Fever
- Faintness or dizziness
- Rapid breathing
These symptoms can indicate a ruptured cyst or an ovarian torsion. Both complications can have serious consequences if not treated early.
Ovarian cyst complications
Most ovarian cysts are benign and naturally go away on their own without treatment. These cysts cause little, if any, symptoms. But in a rare case, your doctor may detect a cancerous cystic ovarian massduring a routine examination. Ovarian torsion is another rare complication of ovarian cysts. This is when a large cyst causes an ovary to twist or move from its original position. Blood supply to the ovary is cut off, and if not treated, it can cause damage or death to the ovarian tissue. Although uncommon, ovarian torsion accounts for nearly 3 percent of emergency gynecologic surgeries. Ruptured cysts, which are also rare, can cause intense pain and internal bleeding. This complication increases your risk of an infection and can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Diagnosing an ovarian cyst
Your doctor can detect an ovarian cyst during a routine pelvic examination. They may notice swelling on one of your ovaries and order an ultrasound test to confirm the presence of a cyst. An ultrasound test (ultrasonography) is an imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of your internal organs. Ultrasound tests help determine the size, location, shape, and composition (solid or fluid filled) of a cyst.